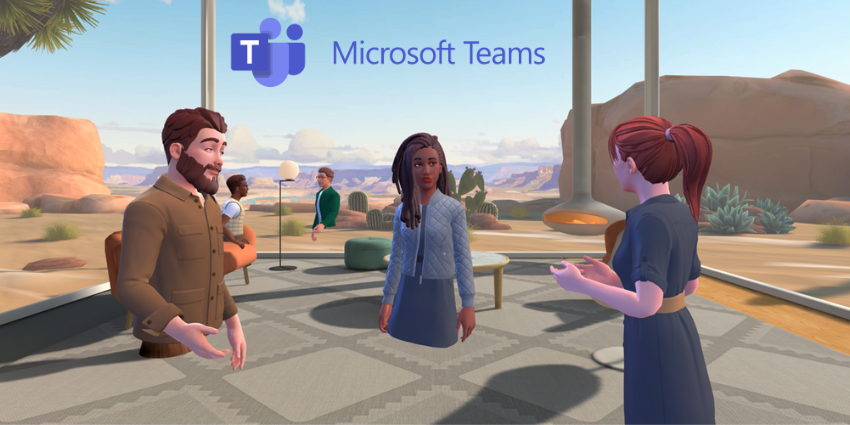
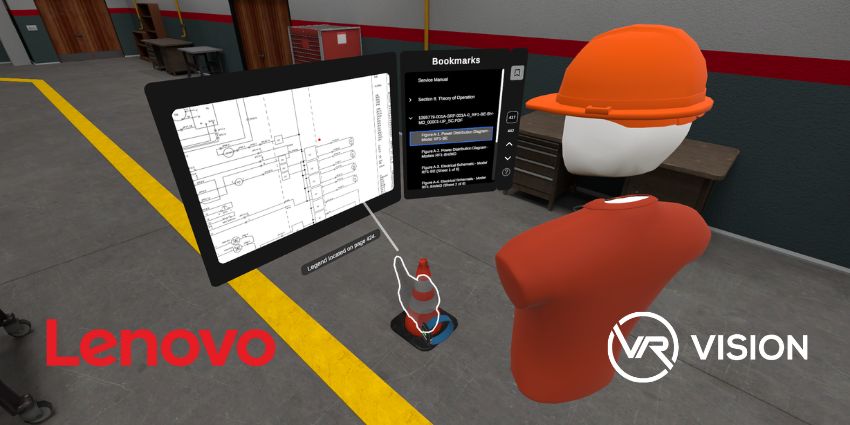
As the Extended Reality landscape continues to evolve, innovators are looking for ways to make our interactions with digital content feel more natural, and streamlined. In the place of clunky plastic controllers and remotes, we’re seeing the rise of hand and eye tracking solutions, allowing users to move more freely throughout the digital world.
Eye and hand tracking technology combines the use of sensors, artificial intelligence, and similar tools to help computer systems understand gaze, gesture, and movement. Using concepts like PCCR (Pupil Center Corneal Reflection), GPS, RGB cameras, and “LiDAR”, XR vendors have created a multitude of ways to immerse users into their XR experiences.
But where exactly can the benefits of hand and eye tracking technology begin to reveal themselves? Here are some of the top use cases for this form of XR innovation.
1. Data Collection and Insights
Hand and eye tracking, at their core, are a form of data collection. They allow companies and computer systems to gather information about a user interacting with virtual content. The more information collected about the user, the more business leaders can unlock useful insights for the development of better experiences and interactions.
In the XR training and education landscape, for instance, hand and eye tracking technology can provide a behind-the-scenes insight into how users might engage with specific machines, technology, and processes. XR motion tracking could even be a way for professionals in the athletic and sporting industry to detect issues with form and posture for each athlete.
The data collection capabilities of eye and hand tracking tools are particularly beneficial for the retail and marketing sectors. By monitoring the movement of a customer’s eyes around a virtual or “metaverse” store, companies can get an insight into what kind of products or advertising efforts capture the most attention. This can lead to the creation of more effective and personalised campaigns for different user groups in the future.
2. Enhanced Human and Robot Interactions
A world where humans and robots live and work side-by-side may still seem like a sci-fi concept to some, but it’s rapidly becoming a part of our current reality. Already, we’re interacting with a range of artificially intelligent bots and automated tools through gestures, and voice. Eye and hand tracking technology will take these communications to the next level.
Gesture control managed by motion or hand tracking technologies may allow future engineers and construction workers to operate machinery from a distance, using IoT connected devices, AI, and edge computing. Eye tracking technology could create a future where we can interact with robotic “humanoids” in the same way we would another person. There’s an excellent insight into how eye tracking might alter educational interactions with robots in the future here.
Eye tracking and hand tracking could also allow for the creation of autonomous vehicles – another form of futuristic robot. In an autonomous car or plane, a sensor system could make it easier for vehicles to detect when a driver isn’t paying attention to potential hazards, so they know when to take the wheel, or slow down.
3. Improved User Interfaces in XR
Perhaps the most significant and obvious use case for hand and eye tracking technology, is improving the user experience we can access in extended reality. While controllers connected to VR devices, AR headsets, and MR solutions can be quite simple to learn, they also detract from the immersive experience. Allowing people to interact with virtual objects using just their hands and vision can bring them deeper into the immersive experience.
By removing the additional layer of technology needed to bridge the virtual and real worlds, vendors in the XR space can create more meaningful experiences. Professionals learning how to perform surgeries in a VR headset can practice actually moving their hands across a virtual “cadaver”, rather than simply pointing, or clicking with a controller. Users wanting to scan through a document in a mixed reality meeting can simply touch the digital paper and bring it closer to their eyes.
Hand and eye tracking technology could even improve the XR experience for people with disabilities, providing computer programs with the information they need to improve rendering and brightness for people with limited vision, or increase audio when someone “leans in” to the source of a sound.
4. Better Rendering Capabilities
One of the most interesting use cases for hand and eye tracking in the XR landscape, looks at the potential this technology could have on the use of computational resources. As the XR landscape continues to evolve, many companies are struggling to find the processing power and bandwidth they need to produce latency and lag-free experiences for users.
While cloud edge rendering technologies and 5G could assist with these issues, hand and eye tracking could also play a role. Using artificial intelligence algorithms, a system can be programmed to render the most important parts of a virtual environment at the correct times. For instance, if a user was walking through a virtual reality space, the system would place the most focus on rendering data related to what they were looking at, and what they should be hearing in the moment.
This technology, known as “foveated rendering”, means companies can more carefully deliver the right amount of bandwidth to specific portions of a VR, MR, or AR landscape, without compromising on clarity. This could be particularly important in areas where access to computing resources are limited, such as in rural areas.
5. A More Secure, Inclusive Metaverse
Finally, hand and eye tracking technology is also likely to play an important part in the evolution of the “metaverse” – the digital environment where countless workplace and community interactions are set to take place in the future. With eye and hand tracking, people in the metaverse will be able to create more realistic avatars, capable of conveying their facial expressions and gestures.
Eye and hand tracking tools could also help to make these digital environments more secure, with the use of biometric AI. Biometric tools built into XR wearable devices will be able to scan the features of a person’s face or their eyes to determine if they are truly who they claim to be.
As people become more concerned about protecting their identity and personal details in the metaverse, this biometric technology could become increasing more important. It could even be a valuable tool to make the “Metawork” landscapes of tomorrow more secure, by ensuring only the correct people get access to certain documents and data.