Can you think of a couple of ways you could utilize your crypto assets? Lending and borrowing are most likely nowhere near your top mentions, right? Yet, crypto loans are an ever-growing sensation in the nascent crypto industry.
The entire process takes place seamlessly, as it uses smart contracts to match lenders with borrowers. For lenders, this can be a way to earn some passive income, while borrowers can use their crypto without cashing out.
Let’s explore how one of the largest lending platforms, Aave, works and improve our knowledge of crypto lending processes.
Key Takeaways
- Aave is an open-source liquidity platform that allows users to lend or borrow cryptocurrency.
- The platform offers its users three types of loans, namely stable, variable, and flash loans.
- Aave is one of the largest DeFi protocols in the industry, with a market cap of well over $1 billion.
- The native token of the platform is the AAVE token. The token is used to access additional platform functionalities, as well as for governance.
What Is Aave?

Aave is a decentralized lending protocol that allows its users to borrow and lend various cryptocurrencies without the involvement of an intermediary.
This simply means that the transactions are not governed by any central authority. The transactions are, instead, controlled by smart contracts. These smart contracts are responsible for overseeing the distribution and allocation of crypto assets. This is done through a network of computers.
Why Was Aave Protocol Built?
The Aave system was initially built and mainly runs on the Ethereum blockchain, but it has also branched out to six other blockchains like Avalanche, Polygon, and Fantom. There are currently 35 different crypto coins available for lending and 25 cryptocurrencies available for borrowing, and different pools come with different pairs and interest rates.
Aave was created to allow users to either borrow or lend cryptos. Borrowers are required to set down a certain amount as collateral before being allowed to borrow, while lenders can put their cryptocurrency to work and earn some returns.
Borrowers
A user can set particular crypto as collateral and borrow another type of crypto. For example, a borrower may use BAT tokens as collateral and borrow ETH instead. This gives users exposure to several cryptocurrencies without necessarily owning them.
Lenders
Lenders contribute cryptocurrency to the Aave market; this improves liquidity and makes funds available to borrowers. Users that lend their funds to Aave earn passive income for providing liquidity. This income is given in the form of interest.
Aave protocol eliminates the need for any form of middlemen. Everything on the platform is run using smart contracts. Even the interest rates are algorithmically calculated when a borrowing or lending transaction is performed.
For borrowers, the algorithm calculates the interest to be paid by comparing the overall available funds to the funds needed by the user. On the flip side, for lenders, the interest is calculated based on the rate of earning and withdrawal at any point in time.
Who Are the Founders of Aave?
Aave was initially launched in 2017 by Stani Kulechov in Switzerland. Kulechov built Aave while he was still a law student, receiving training at the University of Helsinki. His initial plan was to build a protocol that allowed users to borrow or lend crypto directly. This was to be done in this way; the lenders will post loan offers while the borrowers post loan requests.
This protocol, called ETHLend, was met with a lot of difficulties. The major ones were that adequate liquidity wasn’t being provided to the pool, and it was difficult to match willing lenders with ready borrowers. The bear market also took its toll. The combination of these factors led to its collapse in 2018.
Aave actually started out with the name ETHlend. During the initial coin offering (ICO) in 2017, ETHlend raised a whopping 16.2 million dollars, but that was not all. The company also sold a billion units of its native token, LEND. The token is now known as the AAVE token.
After the collapse, the team reviewed ETHlend in 2019 and changed from the peer-to-peer model to the current peer-to-smart contract model. They also made a decision to change the protocol name to Aave.
From ETHLend to Aave
At the time of the migration from LEND to AAVE, the tokens traded at a ratio of 100 LEND to 1 AAVE. This was done in a bid to reduce the total token supply. After the migration was done, the total supply was pegged at 18 million AAVE cryptocurrencies.
Aave was then officially launched in January 2020. Later in the year, in August, the team announced a version 2 upgrade of the protocol.
Why Was Aave Created?
Aave was created to meet up the increasing demands for decentralized money markets. Many users required a means of borrowing cryptocurrency without needing an intermediary, which was why Aave came to the rescue.
Aave users no longer have their resources managed by a centralized authority. They can now manage their funds and make transactions with them as they deem fit. Users don’t even have to know the identity of the person they are transacting with. Smart contracts do all the work here.
So, anyone with a web3 wallet can comfortably perform borrowing or lending transactions using Aave.
Why Is Aave Popular?
The popularity of Aave has grown due to quite a number of reasons. The protocol has played a key role in the decentralized finance industry in the area of liquidity and technology. It is regarded as one of the topmost-ranked money markets in the industry. As a most recent testament to that, Aave has helped a traditional finance giant J.P. Morgan execute its first DeFi transaction.
Aave makes use of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) to log transactions. This is, however, not the main distinguishing factor of Aave. The protocol allows users to borrow or lend a wide variety of crypto coins, including highly rated ones like Ethereum and USDT, as well as other stablecoins and popular altcoins.
The major reason behind the popularity of Aave is its unique “flash loan” feature. This feature allows users to borrow cryptocurrencies without needing any collateral. The transaction must, however, be completed within the time period of a transaction block.
For flash Aave loans to work, the borrower must place a request, use it, and pay it back (plus a 0.09% fee), all within the same transaction block – in Ethereum’s case, 13 seconds. If the borrower fails to meet up, the transaction is automatically cancelled, and all traces are cleared off like the transaction never happened.
This ensures that both parties (Aave and the borrower) encounter no risk.
Interoperability is also a factor that boosts the popularity of Aave. The decentralized lending protocol can interoperate with a variety of decentralized finance platforms. This singular feature makes it very valuable to users who use Aave to perform their lending and borrowing transactions.
What Is Aave Token?
AAVE is the official governance token of the Aave protocol. This means that AAVE token holders have the power to decide what happens on the network. Ownership of the token gives a user the ability to vote and decide the result of various Aave Improvement Proposals (AIPs) sent across the network.
You should note that one AAVE token is equal to one vote. The more tokens you have, the more votes you can cast.
Aside from the AAVE token, another token (or rather a set of tokens) is also used on the Aave protocol. These are the aTokens. aTokens are usually given to lenders who add to a pool. These tokens are issued to enable lenders to receive their interest for providing liquidity to the pool.
Other benefits are also attached to the ownership of AAVE tokens besides voting. Borrowers who deposit AAVE tokens as collateral usually get automatic discounts on transaction fees. Also, borrowing the AAVE token is usually free of charge.
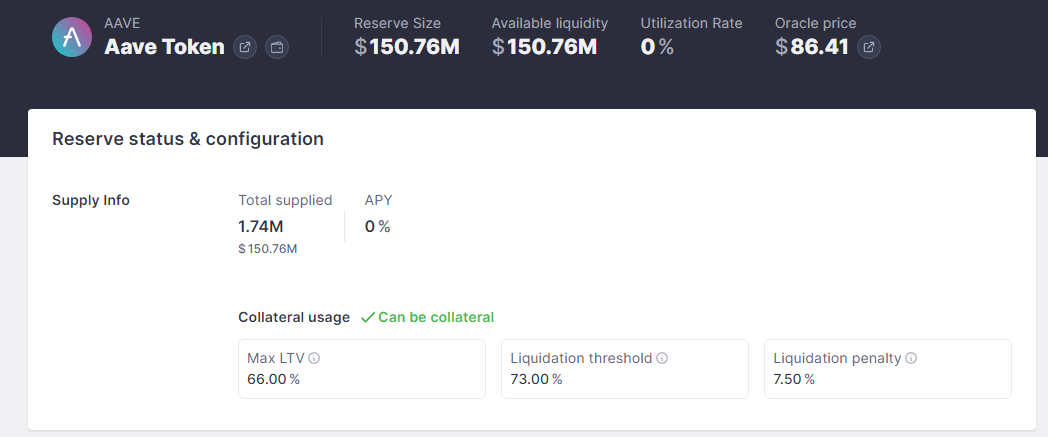
AAVE is a deflationary token. This means that the token is burned constantly. Burning simply means that a particular amount of tokens are sent to a wallet address without a private key to be locked away forever. This will reduce the number of tokens in circulation and will, in turn, force their value to go up.
About 80% of the transaction fees paid are used in the burning process. About 3 million AAVE tokens have also been set aside by the development team to foster the development and growth of the protocol. These coins are kept in Aave’s Ecosystem Reserve Contract.
AAVE token is currently one of the biggest DeFi tokens in terms of market cap. You can trade, exchange, and buy AAVE tokens on several reputable crypto exchanges. You can store your AAVE on any Ethereum-supported blockchain wallet.
How Many AAVE Tokens Are in Circulation?
The maximum supply cap of AAVE is pegged at 16 million tokens. However, out of this number, only about 12.5 million coins are currently in circulation.
The majority of the amount generated from the payment of transaction fees is used to buy back the AAVE token, which would then be burned. This process regulates the number of tokens in circulation, and also contributes to the liquidity of the pool.
The market cap of the AAVE token is determined by multiplying the circulating supply with the token’s market price at any given time. The market rank of any coin is determined by the market cap. The higher the value of the market cap, the higher the rank of the crypto in the market.
What Gives AAVE Tokens Value?
The value of AAVE is tied to its utility. The Aave protocol has a lot of use cases and features that make it even more valuable. The value of the token is also tied to its supply, which is capped at a fixed value of 16 million.
Aave’s DeFi protocol system uses 80% of the fees to purchase AAVE tokens and burn them. This lowers the number of tokens in circulation, which boosts the overall value of the token. The leftover 20% of transaction fees are used to give incentives or rewards to those who lend funds to the liquidity pool.
The popularity and widespread acceptance also directly affect its value. The more people use the protocol, the higher its value.
How Does Aave Work?
Aave functions as a decentralized money market. Rather than connecting individual lenders to borrowers, Aave works using liquidity pools. Here, lenders can add their crypto to the Aave pools, after which they earn rewards based on the amount they deposited.
The pools are algorithmically maintained, and the loans are also automated without any third-party interference. The loans generally come in types:
The loans are also available in several different cryptocurrencies, including BAT and LINK.
Each cryptocurrency has its unique borrowing rate, all of which are listed on Aave’s official website. Rates are calculated based on the forces of supply and demand. If the demand is higher, the interest rate is raised to encourage lenders to deposit more of that crypto.
On the other hand, if the supply of particular crypto is higher than its demand, interest rates are lowered to encourage users to borrow that crypto.
When performing any transaction on Aave, you get rewarded with aTokens, irrespective of whether the deposited funds were meant for lending or borrowing.
Each cryptocurrency has its own aToken. For instance, a deposit of ETH will result in aETH, while a deposit of BAT will give aBAT. These tokens are in equal ratio (1:1) with the value of the asset in question.
These tokens can be stored in cryptocurrency wallets, exchanged, and even traded. This will give users the opportunity to access a wide range of cryptocurrencies without necessarily owning them.
As earlier stated, borrowers are required to deposit collateral before being allowed to borrow. It should, however, be noted that the loans are overcollateralized. What this means is that the collateral is expected to be more in value than the amount to be borrowed.
This Aave loaning system is a good option for investors who need liquidity but do not want to sell off their crypto assets outright. After being deposited, the collateral is handed over to the lender to keep. And if the borrower cannot return the assets within the specified time period, the lender keeps the collateral.
Aave runs on a noncustodial system. This simply means that the contributors to the liquidity pool do not outrightly give up the ownership of their digital assets.
Volatility is a factor that greatly affects cryptocurrency assets. Measures have been put in place to mitigate the effects.
If the crypto’s value increases after depositing the collateral, the initial deposit will also increase in value and will be collected by the borrower after repaying the loan.
If the value decreases below 82.5%, the deposit is lost to the protocol and given to the lender.
Reserves
The crypto market can be extremely volatile, and extreme market swings can turn a business like Aave down the drain. To avoid this, Aave has reserved funds for liquidity pools. This fund is worth 3 million AAVE tokens and acts as a buffer for lenders.
Oracles
Aave can also be used to identify the real-time value of collateralized assets. In collaboration with Chainlink, Aave acts as an oracle to communicate with different blockchains.
Flash Loans
The crypto lending scene changed when Aave introduced flash loans. These are loans that must be repaid within one block and can be used to leverage discrepancies in crypto prices across different exchanges.
Interest Rate Switching
Additionally, users get the option to change their interest rate structure. Aave lets you select either constant or fluctuating rates whenever you like. Continually changing rates are determined by the liquidity pool’s demand. In contrast, stable rates are based on an item’s average interest rate over the previous 30 days.
Aave Pros and Cons
As with every other DeFi protocol, Aave has its pros and cons.
Aave Pros
Strong institutional backing
Aave is backed by many credible crypto institutions. Winklevoss Capital and DTC capital are two popular ones. With this strong backing, it is easier to trust the Aave developmental team in the time of an upgrade.
Multi-faceted uses
To the natural mind, Aave is used to get loans, but having flash loans is more than a glaring advantage. Flash loans are different from normal loans because the loans must be repaid in one block and can help increase gains through scalping little discrepancy in crypto prices.
Aave Cons
Over-collateralization
Aave’s business model requires the over-collateralization of loans. Although it protects the system, this model means average users cannot take loans beyond what they already own.
Low-interest rates
Aave offers low-interest rates. While this might attract borrowers, the core of the system, Lenders, might favor competition with higher rates.
Is Aave Safe?
The Aave protocol is highly secured. It periodically goes through periodic audits to ensure its smart contract is uncompromised, and lenders and borrowers can seamlessly use the platform for their lending and borrowing activities. Loans are almost always overcollateralized to avoid a case where the Aave platform does not have enough liquidity. This makes the platform continue running even in the likely event of loan default. Another way Aave always ensures positive liquidation is through a collateral threshold. This is relevant because the smart contract automatically puts loans in liquidation once they fall below this limit.
The platform also uses reserve liquidity pools that employ these funds to fend off market turbulence. The reserves furthermore act as protection for lenders whose money will be accessible when they want to withdraw it from the liquidity pools.
Bottom Line
Lending and borrowing are two ‘crypto languages’ that will not be going out of vogue in the cryptocurrency market. Like in the traditional market, traders will always have a need for loans, either to leverage arbitrage opportunities or to get other things without liquidating their crypto holdings. Aave has positioned itself strategically through oracles, flash loans, and its interest-bearing tokens, and it is interesting to see how things play out after this current crypto bear market.







